Vaccination is a non-negotiable part of any successful beef operation, but it’s also one of the most commonly mismanaged. From missed boosters to undocumented doses, gaps in protocol can leave even well-bred cattle exposed to preventable diseases. According to research published in Frontiers in Veterinary Science, inconsistent application of beef cattle vaccines continues to contribute to avoidable losses, especially from respiratory pathogens like BVDV and M. haemolytica.
The problem isn’t that producers don’t value vaccination; it’s that managing schedules, recording treatments, and ensuring withdrawal compliance get increasingly complex with herd size and labor challenges. Across cow-calf and stocker operations alike, the need for structured beef cattle vaccines’ protocols, designed by age, environment, and disease risk, is more urgent than ever.
In this blog, we’ll walk through the recommended beef cattle vaccines schedule by lifecycle stage, outline core protocols that align with veterinary guidance, and highlight where most operations lose consistency.
Essential Beef Cattle Vaccines & Timing Guidelines
For producers already vaccinating their herds, the next layer of value lies in precision, knowing which vaccines matter most at each stage, and aligning your protocol with the actual disease pressure on your operation. It’s not about the right ones, at the right time.
Here’s a stage-by-stage breakdown that reflects how today’s successful beef operations are building out smarter protocols:
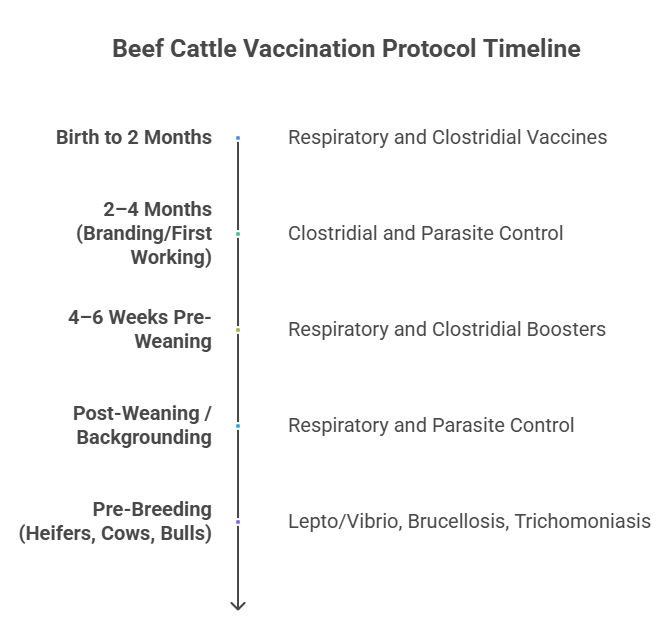
Birth to 2 Months: Early Risk Management
Calves face early exposure to pathogens long before they’re weaned. At this stage:
- Intranasal IBR, PI3, BRSV vaccines help establish respiratory immunity before maternal antibodies wear off.
- Clostridial (7- or 8-way) vaccines (including protection against blackleg) are often introduced in operations with known soil exposure.
- Brucellosis vaccination is required for heifers in many states, typically between 4 and 12 months, and administered by accredited vets.
2–4 Months (Branding or First Working): Core Immunization Begins
This is the first structured opportunity to build baseline protection:
- Modified-live respiratory vaccines covering IBR, BVD Types 1 & 2, PI3, BRSV.
- M. haemolytica/Pasteurella multocida if stress or commingling is likely.
- Clostridial booster to extend coverage.
- Leptospirosis for replacement heifers in endemic areas.
- Begin pinkeye protection if pasture conditions warrant it.
Many producers use data-driven health monitoring to evaluate vaccine details by time, gender, and response and adjust protocol by pasture group or calf source.
4–6 Weeks Before Weaning: Booster + Risk-Based Additions
This stage is where timing becomes critical:
- Re-administer respiratory and clostridial vaccines.
- Pinkeye, Histophilus somni, and pasturella may be introduced depending on exposure risk.
- Deworming and delousing programs may be integrated here.
- Review timing for implant programs and antibiotic withdrawal requirements.
Effective producers often rely on digital health records to track booster windows and ensure proper withdrawal before sale.
Post-Weaning / Backgrounding: Stabilization Before the Next Phase
This phase varies widely based on sale plans, grazing, or feeding environment:
- Repeat the respiratory complex for high-risk calves.
- Administer lepto/vibrio vaccines if calves are being retained as replacements.
- Apply internal/external parasite control matched to the season.
Pre-Breeding: Reproductive Health Coverage
This round focuses on fertility and fetal protection:
- Leptospirosis + Campylobacter (Vibrio) – critical for open cows and virgin heifers.
- BVD and IBR – ensure coverage before breeding; avoid modified-live if pregnant and unconditioned.
- Bulls may receive additional trichomoniasis vaccine depending on regional requirements.
A well-executed beef cattle vaccination schedule and program protects more than just lungs; it supports conception rates, reduces treatment costs, and positions your herd for better weight gain and fewer market disruptions. And the more consistent your records, the easier it is to prove and improve your program over time.
Building a Herd-Specific Protocol: Factors to Consider
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to beef cattle vaccines. A protocol that works well in Kansas may not hold up in Montana, and what protects calves may not be sufficient for breeding cows or bulls. To reduce gaps in immunity and improve outcomes, your vaccination plan should reflect real-world factors tied to your specific herd, region, and management style.
1. Regional Disease Pressure & Biosecurity Risk
Vaccination protocols should always be adjusted based on your local disease landscape. Herds in areas with endemic BVD-PI, Johne’s, or footrot will require added coverage or earlier dosing. If you’re purchasing calves or operating near shared grazing grounds, biosecurity risk jumps significantly. Testing, isolation, and vaccination should work in tandem, not as isolated strategies.
2. Animal Class and Timing Considerations
Heifers, mature cows, bulls, and calves all have different immunological windows and exposure risks. Replacement females need beef cattle vaccines that support reproductive success (e.g., leptospirosis and vibriosis), while bulls may require region-specific vaccines like trichomoniasis. Delays in pre-breeding or post-weaning boosters can significantly undermine overall protocol efficacy.
3. Proper Handling, Storage & Withdrawal Compliance
Vaccines lose potency quickly when exposed to temperature swings or used past expiration. Following BQA handling standards is just as important as the vaccine itself. Equally important: tracking meat withdrawal periods for every product used. Many producers, ranchers and amaller feedlots now rely on digital feedlot checklists to ensure storage conditions and withdrawal timelines are monitored accurately, especially during busy working days.
4. Stress Management During Vaccination Events
Stress suppresses immune response, and poor timing during weaning, transport, or extreme heat can reduce the efficacy of beef cattle vaccines. Integrating low-stress handling techniques, spacing out vaccinations from stressful events, and allowing recovery time are best practices. Think of timing and technique as equal partners in immunity, not afterthoughts.
Pro Tip: A well-structured, adaptable protocol is only as strong as the records behind it. Tools like cattle record-keeping software can help producers manage vaccine types, timing, storage compliance, and animal-specific notes, all in one place.
Common Vaccination Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Even well-intentioned protocols can fall apart in execution. Many producers use the right beef cattle vaccines but still experience preventable disease events due to avoidable mistakes in timing, handling, or record keeping. Spotting these blind spots early can save you from performance losses, treatment costs, and regulatory issues down the line.
Mistake #1: Poor Timing or Missed Boosters
It’s easy to get off track during calving, branding, or weaning season. But administering beef cattle vaccines too close to high-stress events, or missing booster windows, reduces immunity and opens the door to respiratory disease outbreaks. Calendar-based scheduling isn’t enough. Producers who use smart cattle health monitoring tools have better visibility on when each animal is actually due, not just when it’s convenient.
Mistake #2: Incorrect Handling and Application
Common errors like reusing dirty needles, injecting via the wrong route (e.g., IM instead of subcutaneous), or drawing from expired bottles can all weaken vaccine performance and increase tissue damage risk. BQA guidelines are clear, but fatigue and multitasking often lead to skipped steps. Training refreshers and pre-checks before each working session are essential safeguards.
Mistake #3: Incomplete Documentation & Zero Traceability
The costliest mistake often comes later, when a recall, audit, or treatment review requires hard proof. Without a documented history of beef cattle vaccines tied to individual animals, it’s nearly impossible to track compliance or prove withdrawal timelines. Systems give ranches a reliable way to log vaccination events by animal ID, capture product batch details, and generate exportable reports when needed.
Folio3 Cattlytics in Action: Digital Vaccination Tools, Built for Beef Herd Health
When you’re managing thousands of head across multiple pastures or pens, keeping up with beef cattle vaccines manually is not only inefficient, it puts your herd at risk. Cattlytics provides producers with a smarter way to plan, execute, and document every vaccine event across all animal classes, with real-time accountability built in.
Cattle health management software is more than a working system built to reflect how real ranches run health protocols, respond to stress windows, and prepare for audits or buyer traceability.
Step-by-Step: Implementing a Vaccination Schedule with Digital Tools
A smooth digital rollout starts with the proper setup and ends with reliable execution from chute-side to summary reports. Here’s how cattle operations are bringing vaccine protocols online using Cattlytics:
- Review herd structure and vet guidance
Define classes (cow-calf, replacement heifers, bulls, stockers) and align protocol timing with disease risk and veterinary input. - Define vaccines, timing, and boosters by class
Assign core vaccines, respiratory, clostridial, lepto, reproductive, by lifecycle stage, with precise intervals and automatic booster planning. - Configure software by herd groups and vaccine types
Organize your herd into logical groups and input vaccine SKUs, dosage units, and withdrawal days. Mobile workflows are activated per group. - Import historical records and future schedules
Upload past vaccination data by animal ID, then set upcoming protocols, visible to all handlers across locations. - Enable offline data capturing
During working events when there is no internet, staff can record vaccines in offline mode. - Monitor vaccine performance and refine over time
Evaluate outcomes by group or animal, note adverse reactions, and adjust schedules based on field results and seasonal risk changes.
Real ROI & Health Benefits from Automation
Digitizing beef cattle vaccines isn’t just about convenience; it directly impacts herd health, labor efficiency, and operational control. Here’s what producers see after implementation:
- Stronger Immunity Across Groups
Timely boosters and age-aligned scheduling prevent lapses, reducing BRD flare-ups, reproductive losses, and retreatments. - Labor Savings & Reduced Manual Entry
Teams log events faster, avoid transcription errors, and eliminate backlogs from paper sheets or spreadsheets. - Full Traceability for Compliance & Sale Certainty
With one-click access to vaccine logs, lot numbers, and withdrawal timelines, operations are always audit-ready and more attractive to verified beef buyers. - Pattern Recognition to Improve Protocols
Over time, producers gain visibility into which vaccines deliver the best outcomes by source, season, or class, enabling more targeted protocols. - Lower Treatment Costs, Fewer Outbreaks
Proactive management reduces emergency treatment costs, chronic conditions, and weight loss from preventable disease events.
Measuring Success: What KPIs to Track
To evaluate whether your digital vaccine program is delivering value, the following metrics offer clear, quantifiable insights:
- Vaccination Compliance Rate
Percentage of animals vaccinated on schedule, including boosters, monitored in real-time. - Disease Incidence Reduction
Track confirmed cases of BRD, clostridial disease, or lepto against baseline historical data. - Vet and Health Treatment Cost Trends
Monitor per-head veterinary costs, retreatment rates, and dosage frequency over time. - Animal Performance Post-Vaccination
Measure average daily gain (ADG), conception rates, or feed conversion ratios for animals under structured vaccine protocols. - Audit & Certification Readiness
Review traceability logs, product usage history, and withdrawal compliance, ensuring alignment with BQA and processor demands.
With Folio3 Cattlytics, managing beef cattle vaccines goes beyond basic tracking; it becomes a system for continuous optimization and improvement. From scheduling to post-vaccination insights, it turns beef cattle vaccines into a driver of both herd health and operational performance.
Conclusion
A successful beef cattle vaccines program isn’t defined by the number of doses given, it’s measured by how well it aligns with real herd needs, evolving disease pressure, and operational realities on the ground. For producers managing tight working schedules, multi-site herds, or growing traceability demands, the shift toward structured, digital vaccination management isn’t a future idea, it’s already becoming the industry baseline.
By building protocols around animal class, local risk, and real-time data, beef operations gain more than just health protection, they gain control over costs, consistency in record keeping, and credibility with buyers and regulators. When beef cattle vaccines are delivered on time, documented accurately, and reviewed through the lens of herd-level outcomes, they stop being just a health task and start becoming a performance tool. Investing in systems that support this process, from protocol setup to post-treatment reporting, is how modern producers turn beef cattle vaccines management into a competitive advantage that scales with their business.
FAQs
What Is a Typical Beef Cattle Vaccination Schedule?
A typical beef cattle vaccination schedule begins at birth with intranasal respiratory vaccines and progresses through branding (2–4 months), pre-weaning, post-weaning, and pre-breeding phases. Each stage targets specific risks like clostridial diseases, BRD, lepto, and reproductive pathogens, depending on age, stress events, and regional exposure.
How Do I Create An Effective Herd Vaccination Protocol?
To build effective herd vaccination protocols, segment your cattle by class (calves, heifers, cows, bulls), consult your veterinarian, and tailor vaccine timing to local disease risks. Include boosters, withdrawal tracking, and recordkeeping. Digital tools like Cattlytics help ensure consistency and compliance across groups and seasons.
Can I Automate Vaccine Scheduling For Livestock Operations?
Yes, many producers now rely on automated vaccine scheduling for livestock to reduce manual tracking. Systems like Cattlytics let you assign vaccines by herd group, auto-calculate booster dates, and flag missed events, improving both efficiency and herd health outcomes.
Do Cattle Vaccination Systems Send Reminders For Upcoming Doses?
Modern platforms like Cattlytics offer vaccination reminders for cattle, alerting you when animals are due for initial doses or boosters. These reminders can be triggered by age, weight, or time since last dose, ensuring protocols stay on track and nothing is missed during busy handling periods.
Why Is Digital Vaccine Tracking Better Than Paper Logs?
Digital tracking improves accuracy, audit-readiness, and compliance. It also links each animal’s history to withdrawal timelines and outcomes. This makes it easier to manage a complex beef cattle vaccination schedule and reduce health risks caused by missed or late vaccinations.
